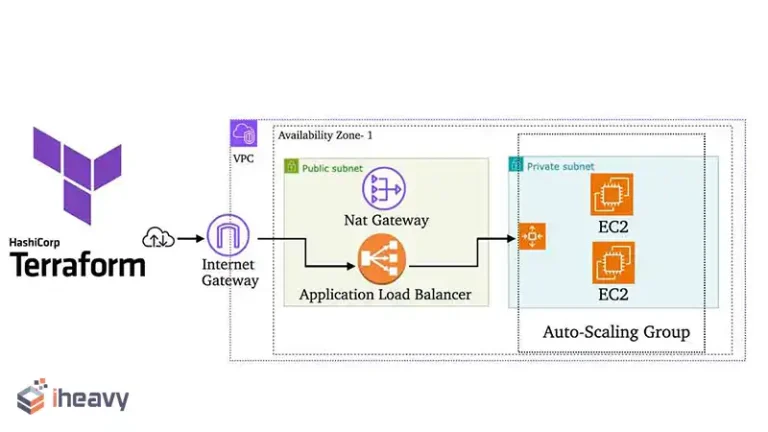
In Depth Comparison of Security Issues: Public Vs Private Vs Hybrid Cloud Computing
Security challenges in public clouds include external network vulnerability and shared resource risks, demanding careful vendor scrutiny. Private clouds face internal threats with a focus on robust network security, while hybrid clouds aim to secure connections between public and private components.
Public clouds adhere to industry regulations, while private clouds manage internal compliance. Both face data residency concerns. Mitigating risks involves regular audits, robust authentication, employee training, and dynamic security policies for diverse cloud environments.
So, what should be best to tackle your security concerns needs more care on comparison; hence emerges the rest of the article.
Public and Private and Hybrid Cloud Security
Public clouds offer scalability and cost-effectiveness, but this accessibility comes with its set of security challenges. Issues like data breaches and unauthorized access can be heightened due to the shared nature of resources in a public cloud setting.
Contrary to public clouds, private clouds operate within a dedicated environment, providing a higher level of control. Internal threats, compliance issues, and misconfigurations are potential pitfalls that demand attention.
Combining the best of both worlds, hybrid clouds leverage both public and private infrastructure. Interconnecting these environments necessitates robust measures to safeguard data during transit and maintain consistent security policies.
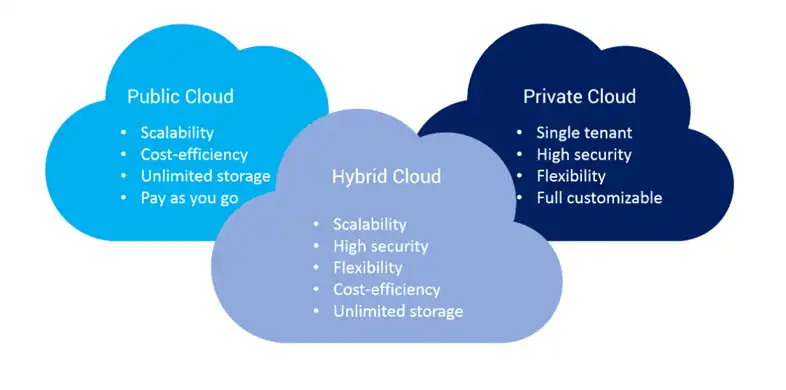
Figure: Cloud classifications.
Security Challenges Across Cloud Models
A number of challenges are discussed in the following:
Data Encryption
Ensuring data integrity is a paramount concern. Encryption is crucial, especially in public clouds where data travels through external networks. Private and hybrid clouds must also implement robust encryption protocols to protect sensitive information.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Unauthorized access poses a significant threat. IAM solutions become imperative, controlling user access, and mitigating the risk of unauthorized entry. Striking the right balance between accessibility and security is pivotal.
Compliance and Legal Issues
Different cloud models warrant varying compliance requirements. Public clouds may need to adhere to industry regulations, while private clouds might face internal compliance challenges. Navigating this regulatory maze is critical to avoiding legal pitfalls.
Data Residency and Jurisdiction
Understanding where data resides is crucial for compliance and security. Public clouds may store data in multiple locations, raising concerns about jurisdiction. Private clouds, while more controlled, still need to address data residency issues.
Network Security
Public clouds rely on external networks, making them susceptible to cyber threats. Private clouds necessitate robust internal network security, and hybrid clouds must secure the connections between public and private components.
Shared Resources
In public clouds, multiple users share resources, creating a potential security vulnerability. Private clouds, though isolated, can face internal threats. Hybrid clouds grapple with securing shared and dedicated resources simultaneously.
Vendor Security
Public clouds involve third-party vendors, intensifying the importance of scrutinizing their security measures. Private and hybrid clouds require meticulous evaluation of in-house security practices and those of external partners.
Mitigating Security Risks
There are some of the steps that will help to mitigate the security risks:
Regular Audits and Assessments
Frequent security audits and assessments are imperative across all cloud models. Identifying vulnerabilities proactively allows for timely remediation, fortifying the overall security posture.
Robust Authentication Protocols
Implementing multi-factor authentication strengthens user identity verification. This layer of security significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access across public, private, and hybrid cloud environments.
Continuous Employee Training
Human error remains a significant contributor to security breaches. Regular training programs ensure employees are well-versed in security protocols, minimizing the likelihood of unintentional security lapses.
Dynamic Security Policies
Adopting dynamic security policies that adapt to the evolving threat landscape is crucial. This approach ensures that security measures stay resilient against emerging threats across diverse cloud environments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Are public clouds inherently less secure than private clouds?
A: Not necessarily. Public clouds have robust security measures, but the shared nature of resources introduces unique challenges.
Q: How does data residency impact cloud security?
A: Data residency issues arise when data is stored in specific geographic locations. Understanding and complying with regional regulations is crucial.
Q: What is the role of IAM in cloud security?
A: IAM controls user access to resources, mitigating the risk of unauthorized entry and ensuring a secure cloud environment.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, security issues persist as a formidable challenge. Navigating the intricacies of public, private, and hybrid clouds demands a nuanced understanding of the unique threats each model presents. Implementing comprehensive security strategies is not just a necessity but an ongoing commitment to safeguarding digital assets.